Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence that takes advantage of advanced statistical techniques to give computers the ability to learn from data without being explicitly programmed to do so. It lets a system spot patterns and quickly make decisions with little to no human intervention.
How Machine Learning Has Evolved Over Time
Machine learning isn’t a science that is completely new. However, it has gained a lot of momentum lately due to the availability of more powerful computing technologies. Machine learning started out from simple pattern recognition and a theory that computers can be made to learn on their own by being shown data, even if they weren’t programmed to carry out specific tasks with it. Thanks to machine learning, systems can continuously adapt when presented with new data.

The algorithms behind machine learning have been around for decades. What has changed lately is that we now have the ability to apply even more complex calculations to big data faster than ever thought possible. Examples of machine learning applications many people are familiar with include: automatic driverless cars, fraud detection systems used by credit card companies, social media sites showing trending topics and online shopping sites recommending items to their users.
Machine Learning Growing in Popularity
During the last few years, there has been a vastly growing amount of interest in machine learning from organizations in various industries. This is mainly due to the availability of big data, more powerful and cheaper computers to process the data and the affordability of information storage solutions.
Businesses can now work with larger and more complex sets of data, all while expecting fast and accurate results. By building the right model, an organization can take advantage of the power of machine learning to spot profitable opportunities while reducing exposure to risk.
Who Uses Big Data?
Industries that routinely deal with large quantities of data have quickly realized just how valuable machine learning technology can be. It can provide them with valuable real time insights that lets them work more efficiently and be more competitive. Here is an overview of who uses machine learning and how they’re applying it to their industry:

Sales and Marketing
If you’ve ever seen a website recommend an item based on purchases you’ve made before or similar items you’ve looked at during a past visit, it means they were using machine learning to promote items you’re more likely to have an interest in.
Marketers are able to use machine learning to acquire data, analyze it and use it in a way that results in more customized promotional campaigns. The result is advertising and marketing materials that are more relevant to shoppers, making them more likely to make a purchase.
Health Care
The health care industry is adopting machine learning at a rapid pace, mainly as a result of the development of wearable medical devices and sensors providing real time information on a patient’s health. Data collected by these sensors can be very useful for medical professionals, as they can use it to identify trends or find ways to improve treatments.
Financial Services
Machine learning lets businesses in the financial industry make sense of their data by rapidly identifying the most important insights. This can lead to finding previously unknown investment opportunities or help investors by showing them the most profitable trades at crucial moments. Machine learning can also analyze patterns in data to identify high risk clients or transactions, which may be used to prevent fraud.
Government Agencies
Government agencies, like public utilities, are able to benefit from machine learning as they often have large amounts of data coming from a variety of sources. This data can be analyzed in various ways. For example, information coming from sensors can help utilities find ways to prevent waste, boost efficiency and save money.
Popular Machine Learning Methods
There are various machine learning methods out there, but the two most popular are supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Here’s how they work:
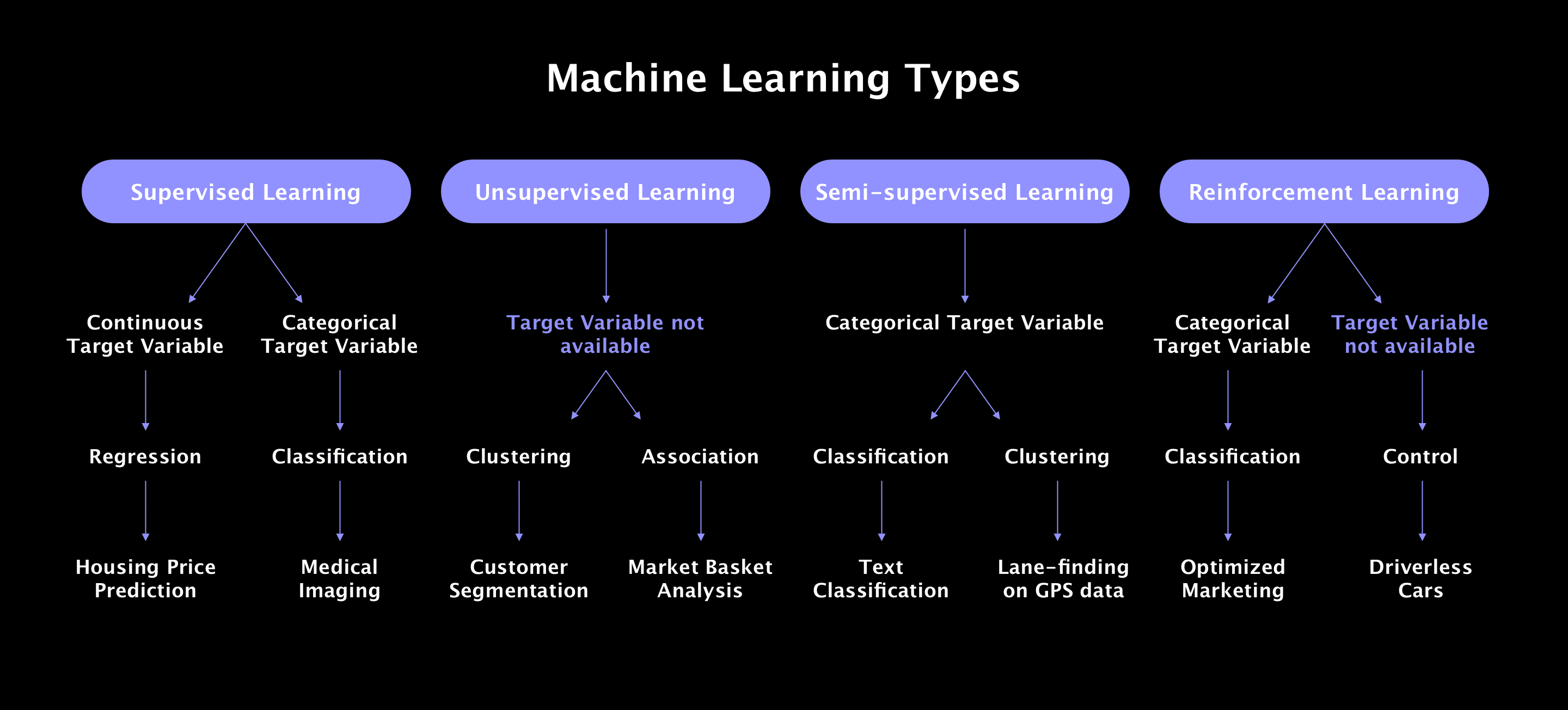
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning uses labeled examples to train a system. It’s used in cases where a desired output is already known in advance. As it learns, the algorithm receives many inputs together with the right outputs. It perfects its model by comparing its own output with the correct one to spot errors.
Supervised learning is often used in applications where past events are likely to predict future ones. For example, it can help an insurance company determine which customers are likely to file a claim in the near future.
Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning, the system doesn’t know which answer is the right one and must figure it out on its own. It will have to explore the data and find some kind of structure within it. A popular example of unsupervised learning is systems being used for marketing campaigns identifying customers with similar attributes and segmenting them so they can receive the right kind of marketing materials.

