Low-Cost DAQ Devices
Data acquisition (DAQ) is a run-of-the-mill concept in most industrial, scientific, and engineering settings where the measurement of environmental factors is fundamental to experiments and processes. Embedded systems juggle the need to manage high-speed analog signals, and therefore similarly employ a DAQ module to save substantial design effort.
The purpose of low-cost DAQ devices is to provide a cost-effective means to collect the data essential to the measurement task easily. Some of the standard signals measured include temperature, voltage, current, heat, among others. The device used has to be well-suited to the specific measured phenomena, while also providing peculiar benefits stemming from its usage.
The most commonly used low-cost DAQ devices are the USB and Ethernet. The USB stands for Universal Serial Bus, which also reflects an industry standard for specific specification protocols. It is essentially a plug-and-play interface that facilitates communication between a computer and peripheral devices.
As low-cost devices, the USB and Ethernet DAQ devices both encompass basic data acquisition tasks such as analog input and analog output, digital I/O, including counter/timers. Other low-cost devices include PXI, PXI-Express, PCI, PCI Express.
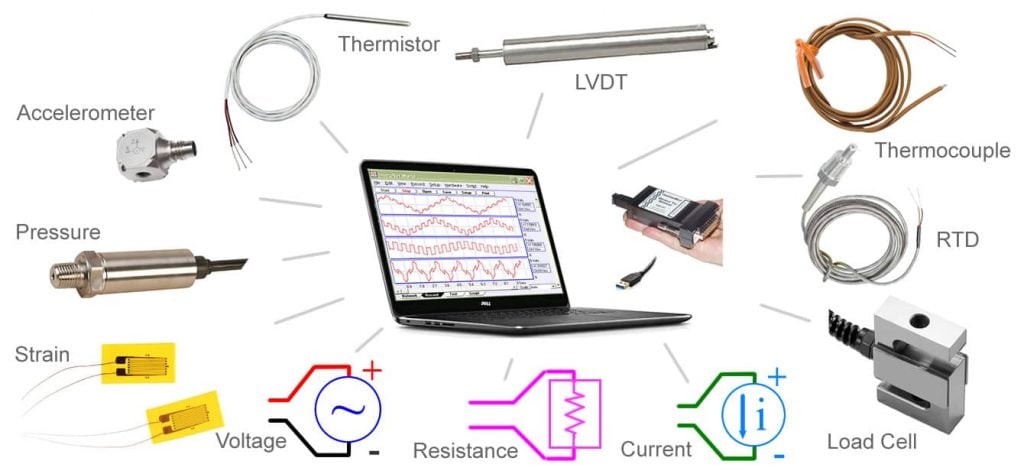
Purpose of USB Low-Cost DAQ Devices
Data acquisition cannot occur in a vacuum. DAQ hardware acts as a point between the signals from the outside world it needs to measure and the computer. Most vendors are increasingly turning to Universal Serial Bus (USB) as their low-cost interface.
There are several reasons for this development, but most center on the advantages it provides for connecting to a data acquisition module over standard buses. For most industrial use cases, the mixture of application simplicity, along with high performance, is a combination too potent to ignore.
Also, the prevalence and familiarity of USB is an advantage due to its use in various computer peripherals such as mice, printers, digital cameras. As a result, you can usually find a wide range of USB data acquisition products for any application and budget with both stand-alone or PC-connected deployment options.
The advantage of DAQ devices that utilize USB solutions is that these provide the opportunity of choice and flexibility to create solutions that are modular and standalone. This fluidity is at the core philosophy of products developed by organizations like DAQiFi, which incorporate the fact that some scenarios do not lend themselves to permit a technician or engineer to possess a computer nearby (for example, on an oil rig.) Therefore, they design their DAQ systems to accommodate this fact.
Features of USB powered Data Acquisition devices
Among the low-cost devices used for DAQ, low-priced USB data acquisition modules are the most flexible and useful for creating applications. Companies, therefore, strive to remain competitive in this domain by offering a diverse range of USB DAQ devices for any application while also accommodating any budget.
These can range from low cost single function modules, up to multi-functional instruments which are both high-precision and high-performance. This is because all the components of a DAQ can be incorporated in a single USB module: analog and digital input/output, counter/timer functions, along with quadrature decoders and tacho inputs.
Most of USB DAQ implementations do not require onerous, additional software or accessories for out-of-the-box measurements.
Many DAQ devices are USB powered, enabling them to avoid additional power supply and, consequently, an excellent fit to design for mobile applications. They also have a robust capacity, with some having as much as 48 analog input channels on each module, possessing sampling rates of up to 10 MS/s per channel, and 24-bit resolution for top-notch accuracy. Other added benefits are its capability of continuous data streaming in realtime to a personal computer.
Some companies even allow you to combine standalone or multiple modules to meet your needs.
Different manufacturers and data acquisition applications have their nomenclature for categorizing their USB series. However, the core features that separate USB DAQs are the quality of their subsystems, namely, the number of analog input/output channels they possess, along with the number of bidirectional digital lines. Then within each, they usually differentiate by their resolution, impedance, and maximum sample rate.
Advantages of USB Low-Cost Data Acquisition devices
- Simplicity: USB only requires four wires while counterpart parallel buses often use 20 or more.
- Proximity: USB enhances flexibility in module placement as it can be as close as 5mm from the hub or controller to which it is attached.
- Portability with easy assembly: This is cardinal for test and measurement applications as USB provides a simple means of deployment, allowing users to move sophisticated applications out from the laboratory and into field operations.
- High-speed data transfer: Almost all USB modules come with full and high-speed data transfer rates. USB 2.0 model ports can reach data transfer rates of 480 Mbits/second. It can also support data acquisition rates of up 400kHz for data streaming applications.
- Carte blanche freedom: Most applications that use low-cost USB DAQ modules allow you to combine multiple modules to facilitate meeting your application needs. Some also have external triggers and a clock to synchronize multiple modules. And these adaptations can be applied to PC-supported or standalone applications.
- Good noise immunity: The noise immunity USB offers is a huge benefit to use in noise-sensitive measurements. Their cables are usually 5mm or less, so while their placement is closer to the signals they are measuring, the I/O circuitry is simultaneously located farther away from the noisy power supplies and computer motherboard. Also, it helps that USBs are fortified by additional isolation from system noise through a physical separation and protective circuitry.
- Channel-to channel galvanic isolation: Not all devices are ideal for use as measuring tools under challenging environments. The high-end applications that operates in oil and gas and power plants are required to have a small size, low EMI, high reliability, and low cost. These requirements are especially challenging for channel-to-channel isolated designs. However, USB devices can provide channel-to-channel galvanic isolation, which permits no direct conduction path, yet allowing data and power to be exchanged.
